This post is also available in: Español
A low AMH diagnosis is a real blow for hopeful parents. Medical treatments to help these women are expensive with very low success rates. Current comprehension on the issue is poorly understood by both patients and doctors alike. Explore the background of low AMH and IVF, so you can make an informed decision. “There is no cure for low AMH.” As far as your doctor knows, they are right.
There is no medical research going on to discover ways of improving women’s low AMH levels.

Anti-Mullerian Hormone underpins the entire growth of your eggs. Without proper AMH levels, your eggs develop like a plant without sunlight. Nothing can get around this reality.
Treating low AMH levels is not even a branch of science. Medicine currently pays it no heed. IVF drugs try to grow as many eggs as they can. IVF success hinges on the ability to develop good eggs. The more eggs they can grow the higher the chance of a successful pregnancy. It has been this way since 1984, and the IVF treatment agenda has not changed.
It is true: Medicine has no treatment to improve AMH levels.
Without this treatment, IVF will always be doomed to failure. IVF drugs do not address low AMH, which is why women always respond so poorly to the procedure. In fact, stimulated IVF cycles lower AMH levels. This is women grow less and less eggs every cycle. If you body is having a hard time growing you one good egg, how is it supposed to grow you ten?

This 3 part series is your essential guide to understanding Artificial Reproductive Technology, IVF and Low AMH.
Part 1: Behind the scenes of IVF: The essence of what, how and why.
Part 2: The secret to IVF success: How to make the grade.
Part 3: How to beat the odds: Smash the cost of IVF.
The evolution of ART and IVF success rates.
25th July 1978 saw the first baby born using Artificial Reproduction Technology (ART). 500000 IVF cycles per year are performed around the world. With an average 100000 IVF babies born, success rates average at 20%. The average cost for an IVF baby is $40000 in first world countries. You are 250% more likely to get pregnant using IVF, than having sex.
This is some statistics IVF clinics are using to sell their services to hopeful parents.
How does IVF outperform nature so spectacularly? When is it worth the money?
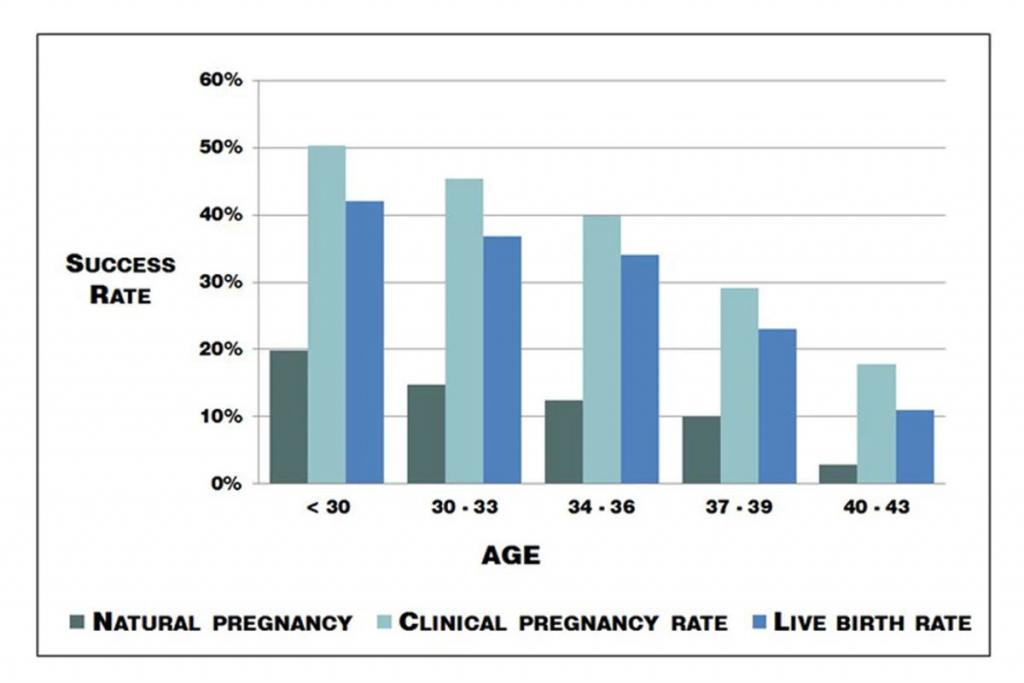
IVF success rates improved from 6% in the 1980s to 20% in 2012. Clinics now tour live birth rates up to 30%. Is this because ART has changed significantly in the last six years? Alternatively, because more people are using it?
More people use IVF now than ever before.
In the 1980s IVF was used only for women with damaged fallopian tubes. These fallopian tubes prevented an ovulated egg from entering the uterus. Natural pregnancy is impossible under these circumstances.
Nowadays women use IVF even when no problems are found, only that they cannot seem to fall pregnant.
Within four years of the first successful IVF baby, the future of IVF treatment was set. The use of ovarian stimulating drugs allowed doctors to grow more eggs than usual. These extra eggs provided more chances for successful fertilization. With more eggs to fertilize and implant, live birth rates increased. In 1980 you had a 6% chance of a baby using the dominant follicle your ovaries produced. Innovations revolved around improving the quality of ovarian stimulating drugs.
From 1984 to 2012 IVF success rates increased by 12% – 14%.
Studies proved that the more eggs you could grow and harvest in a cycle, the higher the chances of pregnancy. Drugs to develop more eggs has been the focus of IVF treatment ever since. This has not changed since 1984.
To grow more eggs than usual, scientists mimicked the natural hormones the body uses. Higher doses of synthesized gonadotrophin hormones proved useful. In 1984, three mature harvested eggs per cycle were brilliant. Today, an excellent outcome is growing 10 – 15 eggs in one IVF cycle.
hMG, hCG, and GnRH are the synthesized hormones used by IVF. Their job is to mature and harvest more eggs than your ovaries would produce on their own. Variations in quality and dosage of these drugs are the primary differences in global IVF treatment protocols.
How IVF works…exactly
Phase 1. Stimulate the ovaries to grow more eggs
Human Menopausal Gonadotrophin (hMG) injections begin IVF treatment. This starts shortly after the beginning of menstruation. Ovary stimulating hMG is injected daily for 7 – 12 days. hMG is synthesized from the urine of post-menopausal women. It contains varying amounts of Follicular Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). The different values of FSH and LH in the hMG injection can depend on your existing hormone levels. Your hormone blood test results will guide your doctor to the recommended balance.
FSH is produced naturally and released by your pituitary gland. Like the name suggests, it grows your follicles. LH works in concert with FSH to grow your eggs, just at lower levels. Once your eggs reach 14 – 16mm in size LH levels jump dramatically to finalize maturation. FSH does not rise with LH now, having done its job already. Once matured, the ongoing increase in LH creates ovulation.
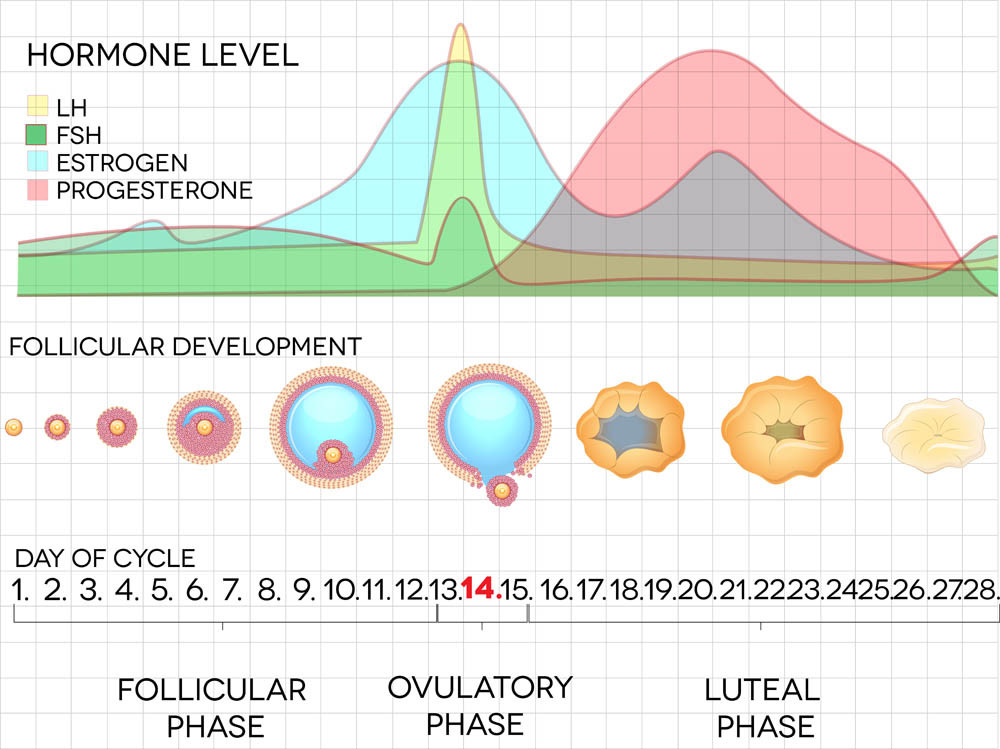
Phase 2. Stimulate the ovaries to mature the eggs
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG injections) are next. hCG is a hormone produced by the placenta of pregnant women. Like hMG, hCG is synthesized from urine, but of pregnant women this time. hCG mimics Leutinizing Hormone (LH) in the body. It is given to finalize the maturation of the viable eggs in preparation for ‘egg pick-up.’ They are also known as the ‘trigger injection.’ There appears to be no difference in any of the brands producing hCG injections. The only variation you may receive is the level of dose.
Phase 3. Stop the ovaries from ovulating
Gonadotrophin-releasing Hormone (GnRH) injections suppress Luteinizing Hormone close to ovulation. IVF doctors do not want the eggs ovulated; they want to harvest them manually. GnRH halts the natural LH surge and prevents ovulation. hCG injections replace natural LH to finish the process of maturing your eggs.
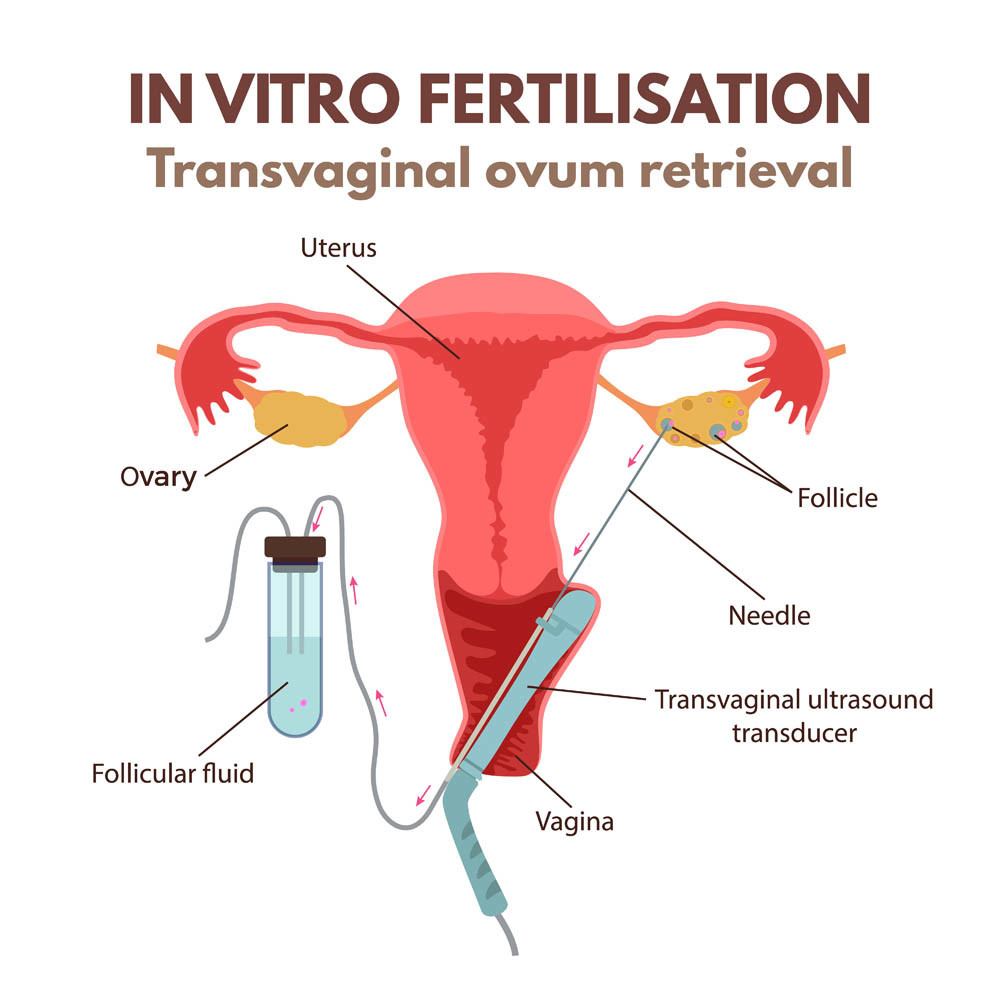
Phase 4. Egg pick up
At this time your IVF doctor will harvest all mature follicles. Once collected there are two options for fertilization. The eggs can be placed in a dish with many sperm and see if fertilization occurs. This is called In Vitro Fertilization. The other is IntraCytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). This is where a single sperm is injected directly into a harvested egg for fertilization.
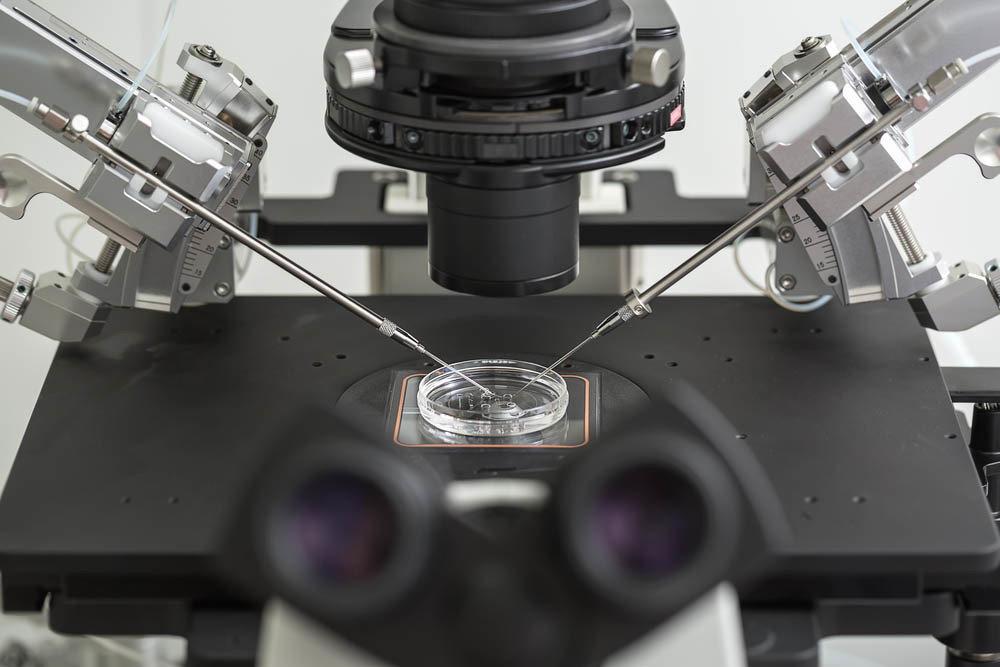

Phase 5. The Blastocyst Games
There is a 3 to 5-day wait to see how the fertilized eggs evolve. High levels of cell division of the fertilized egg determine its level of quality. These are called blastocyst rates. Some doctors choose to return an egg on day 3. Others prefer to wait until day 5. The ongoing health of the fertilized egg is much easier to see on day 5.
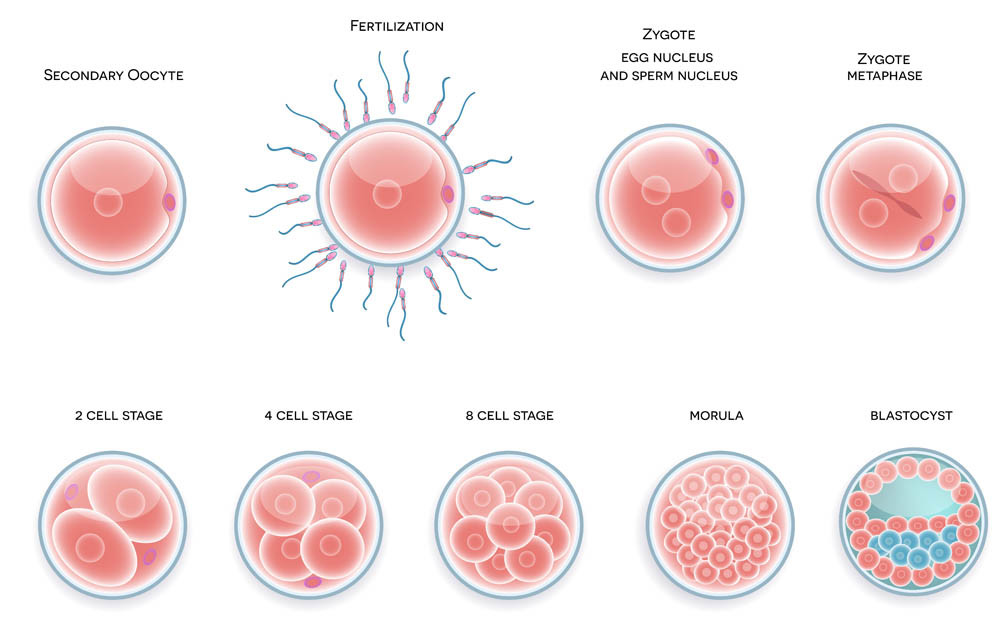
On day 3 or 5 your highest quality blastocyst is prepared for the ‘egg transfer.’ A catheter is inserted into the cervix and the fertilized egg deposited through it. Progesterone is often provided at this stage to continue mimicking natural hormone levels. Fingers crossed for hopeful implantation and a successful pregnancy.
Other good quality eggs left over can be frozen for use on another occasion, if this cycle fails.
Phase 6. The wait
Finger crossed for the pregnancy test two weeks later.
If it has worked; congratulations! Everyone is very happy, and we are also very happy for you too. Wonderful news.
If it has not worked, and you want to know why, the most common answer is, “You just weren’t lucky this time; most likely a genetic problem with the egg. Your chances improve with every cycle you do. Can we book you in next month?”
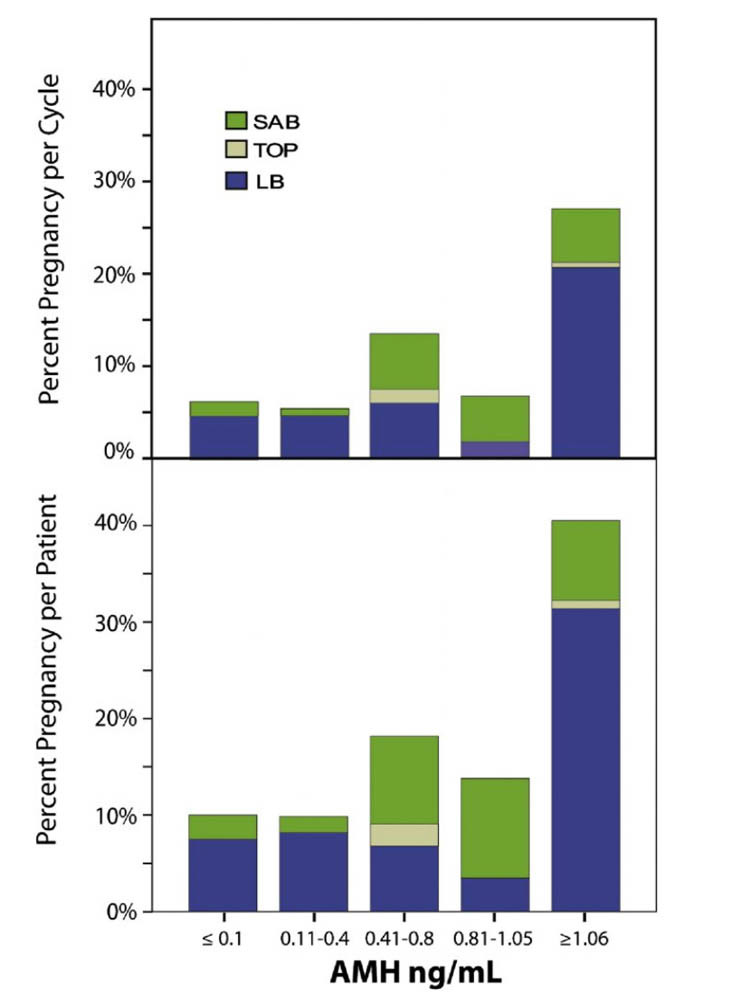
Globally the average IVF live birth rate is 20%. This means that for every 100 IVF cycles performed, only 20 will give birth. If you have low AMH levels, you chances are not this good. IVF is the foremost reproductive technology according to Modern Medicine in the world.
Considering the cost would you like to know how to turn the odds in your favour?
In the next article “ART, IVF and AMH: Your Essential Guide Pt 2,” you will discover the essence of successful IVF pregnancies.


There’s definately a great deal to learn about this issue.
I love all the points you’ve made.
I am glad you enjoyed the article. I believe it is very important to understand what our doctors are doing and why.